|
Hosted Species (last updated June 8 2017)
|
| Clonorchis sinensis |
Trematode |
| Echinostoma caproni |
Trematode |
| Fasciola gigantica |
Trematode |
| Fasciola hepatica |
Trematode |
| Fasciolopsis buski |
Trematode |
| Haplorchis taichui |
Trematode |
| Opisthorchis felineus |
Trematode |
| Opisthorchis viverrini |
Trematode |
| Paragonimus heterotremus |
Trematode |
| Paragonimus kellicotti |
Trematode |
| Paragonimus miyazakii |
Trematode |
| Paragonimus westermani |
Trematode |
| Schistosoma curassoni |
Trematode |
| Schistosoma haematobium |
Trematode |
| Schistosoma japonicum |
Trematode |
| Schistosoma mansoni |
Trematode |
| Schistosoma margrebowiei |
Trematode |
| Schistosoma mattheei |
Trematode |
| Schistosoma rodhaini |
Trematode |
| STrichobilharzia regenti |
Trematode |
|
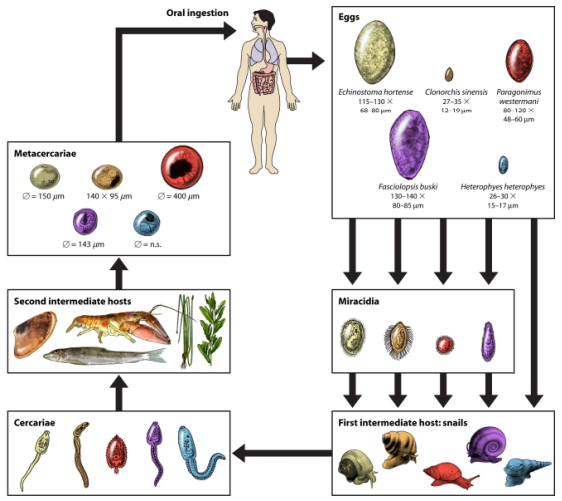
Life cycles of five different food-borne trematodes including intestinal flukes (Echinostoma hortensee, Fasciolopsis buski and Heterophyes heterophyes), a liver fluke (Clonorchis sinensis) and a lung fluke (Paragonimus westermani) (Keiser and Utzinger, 2009).
|
 |
|
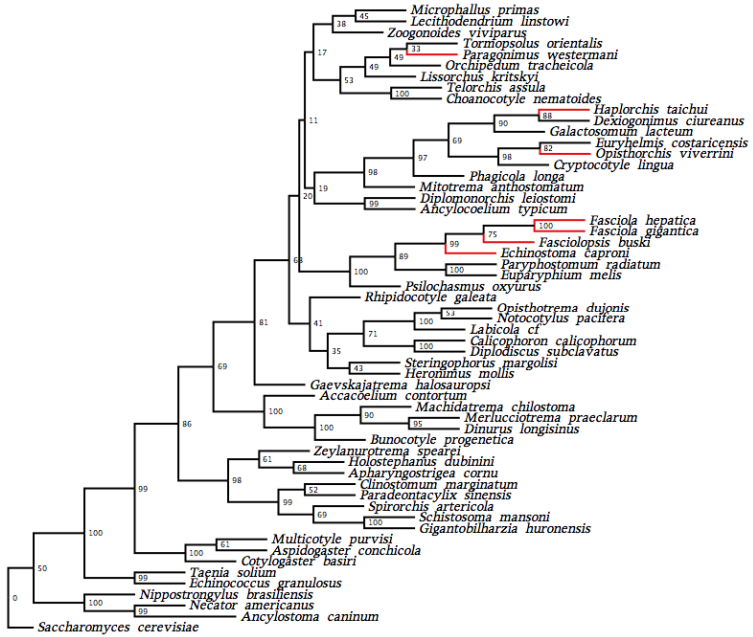
Molecular phylogeny of the class Trematoda based on ribosomal RNA sequence data.
|
 |
|
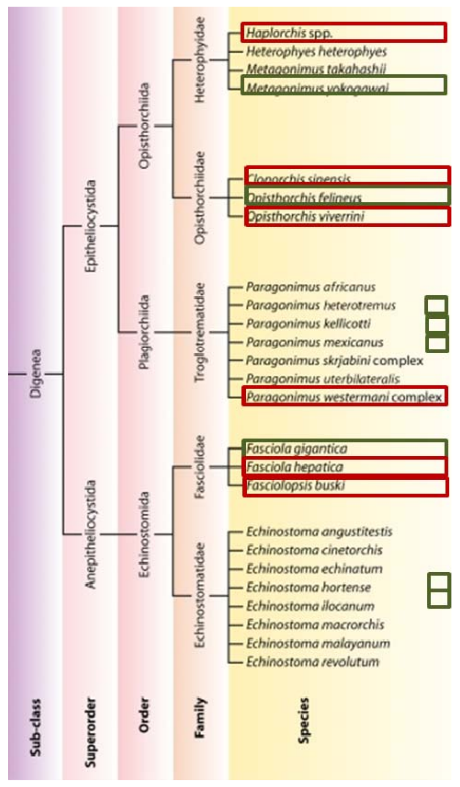
The order Digenea. Species are grouped into major taxonomic groups based on phylogenic analysis of data for the small subunit of ribosomal DNA (SSU) (modified from Keiser and Utzinger, 2009).
|
 |
|
|
|
|




